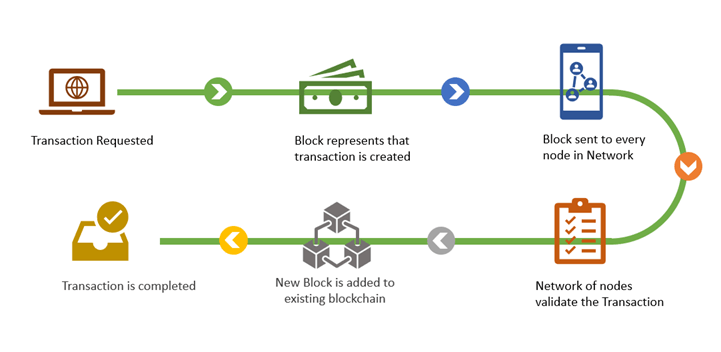
If you are wondering what Blockchain is, I will give you a quick introduction. Blockchain is a data structure that is distributed at once in many different places and as you can’t ever delete from it, it is extremely difficult to make amendments. This makes the record more secure and more trustworthy.
So, what are the kinds of test that you can perform ? You can use the traditional testing, since it is just normal development work with normal testing criteria. So, boundary value analysis, decision tables, test driven development and behavior driven development techniques.
There is also a set of questions that can help you to build your test scenarios, for example:
- How does it handles valid and invalid inputs?
- How does it cope with a wide range of input data?
- How does it handle missing state, or existing state?
- How does it handle error cases?
- How does it handle security and access control?
You don’t need to test the Blockchain because the algorithms are well-established, because it is a distributed system, but the transactions still require some kind of validation. For example, you may need to check if your transaction is valid before it can be approved. There are approval authorities for different blockchains, and they must test the integrity of the transactions.
What is Smart Contract ?
Smart Contract is an API and defines the rules for transactions in a Blockchain network. A Smart Contract is a set of rules in the form of programmable constructs that are capable of automatically enforcing themselves when pre-defined conditions are met.
It has public functions which might be called by anyone registered on the Blockchain network. However, unlike a traditional API, a Smart Contract cannot call external web APIs.
What do you need to know to test Ethereum Smart Contracts ?
Test automation requires that the platform being tested must have hooks so that external automated scripts can instruct the platform, observe the outcome, and verify that the outcome is what is expected. Legacy platforms in banking often do not have these hooks, and that makes automation much more difficult. When you compare smart contracts to older software used in banks, you can automate testing much earlier and much faster.
I will show some of the tools that you can use to perform tests on Blockchain applications:
Ethereum Tester
This github has a project for you to test Ethereum Blockchain Applications. You will need to clone Eth-Tester. The Eth-tester library strictly enforces some input formats and types.
Truffle
Truffle is one of the most popular Ethereum development frameworks and has testing functionality, it is a scaffolding framework for smart contracts used by UI builders. You have the ability to write automated tests for your contracts in both JavaScript and Solidity and get your contracts developed quickly.
Ganache
Ganache is the most-used library for testing Ethereum contracts locally. It mocks a blockchain that gives you access to accounts you can run tests, execute commands, etc.
Populus
By default tests run against an in-memory ethereum blockchain and as you can see here Populus supports writing contracts that are specifically for testing.
Manticore
Manticore is a symbolic execution tool for analysis of binaries and smart contracts. It is supported on Linux and requires Python 2.7. Ubuntu 16.04 is strongly recommended. It has a Python programming interface which can be used to implement custom analyses. You can see more about here on the wiki.
Hyperledger Composer
Hyperledger Composer supports three types of testing: interactive testing, automated unit testing and automated system testing. It’s a framework for rapidly building Blockchain business networks on top of a Blockchain platform, such as Hyperledger Fabric.
This framework allows you to automatically deploy the business network definition, and then interact with it by submitting queries and transactions in order to test how that business network really behaves.
Corda Testing Tools
Corda is a blockchain-inspired, open-source distributed ledger platform. There are several distinct test suites each with a different purpose: Unit tests, Integration tests, Smoke tests, Load tests and other. These tests are mostly written with JUnit and can run via Gradle.
BitcoinJ
This tool BitcoinJ allows you to interact with Bitcoin connecting directly to the bitcoin network. So, you can simulate send and receive transactions in real time, also you don’t need to have a local copy of the Bitcoin Core.
You can follow this guide to get start with this tool.
Resources:
https://www.joecolantonio.com/2018/02/01/blockchain-testing-tools/
https://joecolantonio.com/testtalks/175-blockchain-application-testing-rhian-lewis/
http://searchsoftwarequality.techtarget.com/answer/Heres-everything-you-need-to-know-about-testing-blockchain
https://www.capgemini.com/2017/01/testing-of-smart-contracts-in-the-blockchain-world/
http://www.bcs.org/content/conWebDoc/56020
https://medium.com/@mrsimonstone/test-your-blockchain-business-network-using-hyperledger-composer-c8e8f112da08