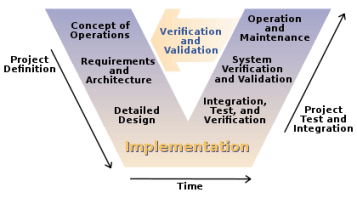
It was the first model of tests, is simple to understand and linear-sequential. You can use the waterfall model when the requirements are very well known, clear and fixed; Product definition is stable; No changes in the scope; You understood the technology; There are no ambiguous requirements; Resources with required expertise are available freely; Project is short.
In Royce’s original waterfall model, the following phases are followed in order:
1- Requirements specification resulting in the product requirements document
2- Design resulting in the software architecture
3- Construction (implementation or coding) resulting in the actual software
4- Integration
5- Testing and debugging
6- Installation
7- Maintenance
Model:

Iterative vs. waterfall
One of the differences between agile and waterfall is that testing of the software is conducted at different stages during the software development life-cycle. In the Waterfall model, there is always a separate testing phase near the completion of an implementation phase. However, in agile development and especially extreme programming, testing is usually done concurrently with coding, or at least, testing jobs start in the early days of iteration.
Advantages?
– This model is simple and easy to understand and use.
– It is easy to manage due to the rigidity of the model – each phase has specific deliverables and a review process.
– In this model phases are processed and completed one at a time. Phases do not overlap.
– Waterfall model works well for smaller projects where requirements are very well understood.
Disadvantages?
– Once an application is in the testing stage, it is very difficult to go back and change something that was not well-thought out in the concept stage.
– No working software is produced until late during the life cycle.
– High amounts of risk and uncertainty.
– Not a good model for complex and object-oriented projects.
– Poor model for long and ongoing projects.
– Not suitable for the projects where requirements are at a moderate to high risk of changing.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agile_software_development#Iterative_vs._waterfall